Published online Jun 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5690
Peer-review started: October 27, 2021
First decision: February 14, 2022
Revised: March 10, 2022
Accepted: April 21, 2022
Article in press: April 21, 2022
Published online: June 16, 2022
Yougui pills have long been used to treat hypothyroidism, usually in combination with levothyroxine sodium in clinical treatment, while their clinical efficacy and safety are still controversial when compared to levothyroxine treatment alone.
To explore the clinical efficacy and safety of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium in the treatment of hypothyroidism.
This meta-analysis was performed in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. Randomized controlled trials on Yougui pills in the treatment of hypothyroidism published from 2008 to May 2021 were searched in a total of 8 databases (4 databases in Chinese and 4 databases in English). The quality of the included studies was evaluated according to the Cochrane risk assessment tool. Weighted mean difference (WMD) was used for continuous variables, and relative risk (RR) was used for binary variables. Data were extracted, and the meta-analysis was conducted with the statistical software of Stata15.0 and RevMan5.0.
A total of 140 articles were retrieved, and 9 of them were finally included, with a total sample size of 936 cases. The main meta-analysis results are as follows: (1) The group of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium had a significantly higher overall response rate than the group of levothyroxine sodium (RR = 1.20, 95%CI 1.12, 1.28, P < 0.00001); (2) Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium achieved significantly better efficacy than levothyroxine sodium alone in alleviating adverse symptoms [standard mean difference (SMD) = -1.10, 95%CI: -1.37, -0.84, P < 0.00001]; (3) The level of thyrotropin stimulating hormone in the group of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium was significantly lower than in the control group of levothyroxine sodium (WMD = -1.38, 95%CI: -2.10, -0.67, P = 0.00001); (4) The level of free triiodothyronine in the group of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium was higher than that in the control group of levothyroxine sodium (WMD = 0.41, 95%CI: 0.03, 0.79, P = 0.03); (5) The level of free thyroxine in the group of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium was significantly higher than that in the control group of levothyroxine sodium (SMD = 0.83, 95%CI: 0.44, 1.22, P ≤ 0.0001); and (6) The adverse reactions in the group of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium were significantly less than those in the control group of levothyroxine sodium (RR = 0.33, 95%CI: 0.20, -0.53, P < 0.00001).
In the treatment of hypothyroidism, the combination of Yougui pills with levothyroxine sodium may be better than levothyroxine sodium treatment alone.
Core Tip: The combined treatment of Yougui pills and levothyroxine sodium can effectively reduce or eliminate the adverse reactions caused by the use of hormones, increase the secretion of hormones in serum and thus significantly improve the clinical symptoms of hypothyroidism. We recommended the use of levothyroxine sodium in combination with Yougui pills in patients with hypothyroidism.
- Citation: Liu XP, Zhou YN, Tan CE. Systematic review of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium in the treatment of hypothyroidism. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(17): 5690-5701
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i17/5690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i17.5690
Hypothyroidism is a condition characterized by impaired metabolism and multisystem function as a result of decreased thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion, insufficient tissue utilization or insufficient biological effects[1,2]. Hypothyroidism is more common in women, with the highest incidence between 30-years-old and 50-years-old, and the incidence of hypothyroidism is rising year by year due to excessive iodine intake, the fast pace of life, pollution of the living environment, etc. Hypothyroidism is characterized by low metabolism, which is accompanied by associated symptoms, including fatigue, hypothermia, delayed response time, memory loss, unresponsiveness, irregular menstruation, mucosal edema, etc and may lead to further complications such as osteoporosis, anemia and hyperlipidemia. Hypothyroidism is related to cardiovascular diseases, including atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease, pericardial effusion and a variety of nonspecific electrocardiogram abnormalities[3,4].
Currently, the treatment of hypothyroidism in Western medicine is mainly based on thyroid hormone replacement therapy, which has a high recurrence rate after withdrawal and prolonged treatment duration, and clinical symptoms are difficult to improve quickly. Excessive doses are likely to induce hyperthyroidism or abnormal bone metabolism. Some patients have poor tolerance with side effects such as insomnia, rapid heart rate or tachycardia and arrhythmia, and in the elderly and patients with heart diseases, angina pectoris or myocardial infarction can be induced[5-7]. Considering the limitations of Western medicine treatment, the combined use of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and Western medicine may bring better efficacy and safety.
Hypothyroidism is classified as a “gall disease” in TCM, and its etiology is related to emotions, dietary injuries and congenital endowments. TCM treatment advocates warming the spleen yang and the kidney yang as the fundamental methods to improve the functions of the various organs of the body. Yougui pills are derived from Jingyue Quanshu written by the Ming Dynasty physician Zhang Jing-Yue, and the whole prescription consists of ten herbs: rehmannia, yam, cornel, wolfberry, antler gum, dodder, eucommia, angelica, cinnamon and aconite. The main effect is to warm the kidney yang, replenish vital essence, nourish the bone marrow and treat the deficiency of kidney yang and the syndrome of declining vital gate fire. Modern pharmacology shows that Yougui pills have the effects of resisting yang deficiency, regulating the endocrine system, protecting the central nervous system, enhancing the body’s immunity and affecting bone metabolism[8,9]. Studies have shown that Yougui pills can be used in combination with Western medicine to produce a synergistic effect, reduce the dosage and hormone usage duration, reduce or eliminate adverse reactions caused by hormone treatment and significantly improve the therapeutic effect of patients[10,11].
Due to the small sample size of previous studies, the value of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium for hypothyroidism remains unclear. This study compared the efficacy and safety of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium and levothyroxine sodium alone in the treatment of hypothyroidism using the meta-analysis method to provide more evidence-based medical evidence and evaluate the value of Yougui pills in hypothyroidism.
Inclusion criteria: (1) The study type was randomized controlled trial (RCT); (2) The research subjects all met the syndrome differentiation of kidney yang deficiency/spleen-kidney yang deficiency in TCM[12] and the diagnostic criteria of hypothyroidism in the Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Thyroid Diseases in China[13]; (3) Intervention measures: Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium were used in the experimental group, whereas levothyroxine sodium was used in the control group. The course of treatment was clear, with explicit efficacy evaluation criteria. There were no restrictions on the use of the blind method, and the language of publication could be either Chinese or English; and (4) Endpoints: the overall response rate (defined as the disappearance or improvement of symptoms and signs after treatment, recovery of thyroid function and other related indicators[10,11]), thyrotropin (TSH), serum levels of free triiodothyronine (FT3), free thyroxine (FT4), TCM symptom scores and safety indicators (adverse reactions after medication). Exclusion criteria: (1) Case reports, case series, letters, comments and review articles; (2) Articles whose data cannot be extracted; (3) Pure abstract papers; (4) Animal or in vitro studies; and (5) Duplicate and irrelevant data.
Two research reviewers independently conducted a literature search in a total of 8 databases: China National Knowledge Internet, China Academic Journals Database (Wanfang Database), Chinese Science and Technology Journals Database (VIP Database), China Biomedical Literature Database, PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library and Web of Science. The retrieval time was set from 2008 to May 25, 2021. The Chinese search terms included (Yougui pills) and (hypothyroidism). The English search terms included Yougui pill, you gui wan, you-gui-wan, ygw herbal preparation hypothyroidism, hypothyroidisms and thyroid-stimulating hormone deficiency; and the English PubMed search strategy is shown in Table 1. There were no age, gender or racial restrictions, but the search language was limited to Chinese and English. According to the difference of each database, the subject words were combined with free words or keywords to conduct the retrieval.
| ID | Query |
| #1 | “you gui wan” [MESH] |
| #2 | (“you gui wan” [ Title/Abstract]) OR (you-gui-wan [Title/Abstract]) OR (ygw herbal preparation [Title/Abstract]) OR (yougui pill [Title/Abstract]) |
| #3 | #1 OR #2 |
| #4 | “hypothyroidism”[MESH] |
| #5 | (((((((hypothyroidism [Title/Abstract]) OR (hypothyroidisms [Title/Abstract])) OR (thyroid-stimulating hormone deficiency [Title/Abstract])) OR (thyroid-stimulating, hormone deficiencies [Title/Abstract])) OR (thyroid stimulating hormone deficiency [Title/Abstract])) OR (thyroid-stimulating hormone deficiencies [Title/Abstract])) OR (tsh deficiency [Title/Abstract])) OR (tsh deficiencies [Title/Abstract]) |
| #6 | #4 OR #5 |
| #7 | #3 AND #6 |
Literature screening, data extraction and quality evaluation were carried out independently by the two authors. Any differences would be resolved through discussion until reaching a consensus. If disagreement persisted, an evidence-based medicine expert would be consulted for a discussion to reach a consensus. The literature quality evaluation was based on the risk of bias assessment tool on RCT (1) in the Cochrane Handbook 5.1.0[14], and the evaluation included the following aspects: (1) Generation of random sequence; (2) Allocation concealment; (3) Whether the blind method was implemented for the subjects and relevant test personnel; (4) Blind evaluation of effect indicators; (5) Incomplete result data; (6) Selective reporting of results; and (7) Other sources of bias. The evaluation results were represented by the terms “high risk,” “unclear” and “low risk.”
Meta-analysis was performed using Stata 15.0 and RevMan5.0 software. Weighted mean difference was used for continuous variables. In order to eliminate the influence of the dimension, FT4 and TCM syndrome scores in this study were expressed as standard mean difference (SMD) and 95%CI. Binary variables were represented by relative risk (RR) and its 95%CI. The heterogeneity test was performed among the studies. When P ≥ 0.1 and I2 < 50%, the heterogeneity was regarded as low, and the fixed-effect model was adopted. Whereas, when P < 0.1 and I2 > 50%, the heterogeneity was considered to exist, and then subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis were adopted to explore the source of heterogeneity. Furthermore, if the source of heterogeneity could not be determined, a random-effect model was used to conduct a meta-analysis of the literature. Begg’s and Egger’s tests, as well as funnel plots, were used to assess the publication bias of the included studies. P < 0.05 indicated the presence of publication bias, whereas P > 0.05 indicated no publication bias.
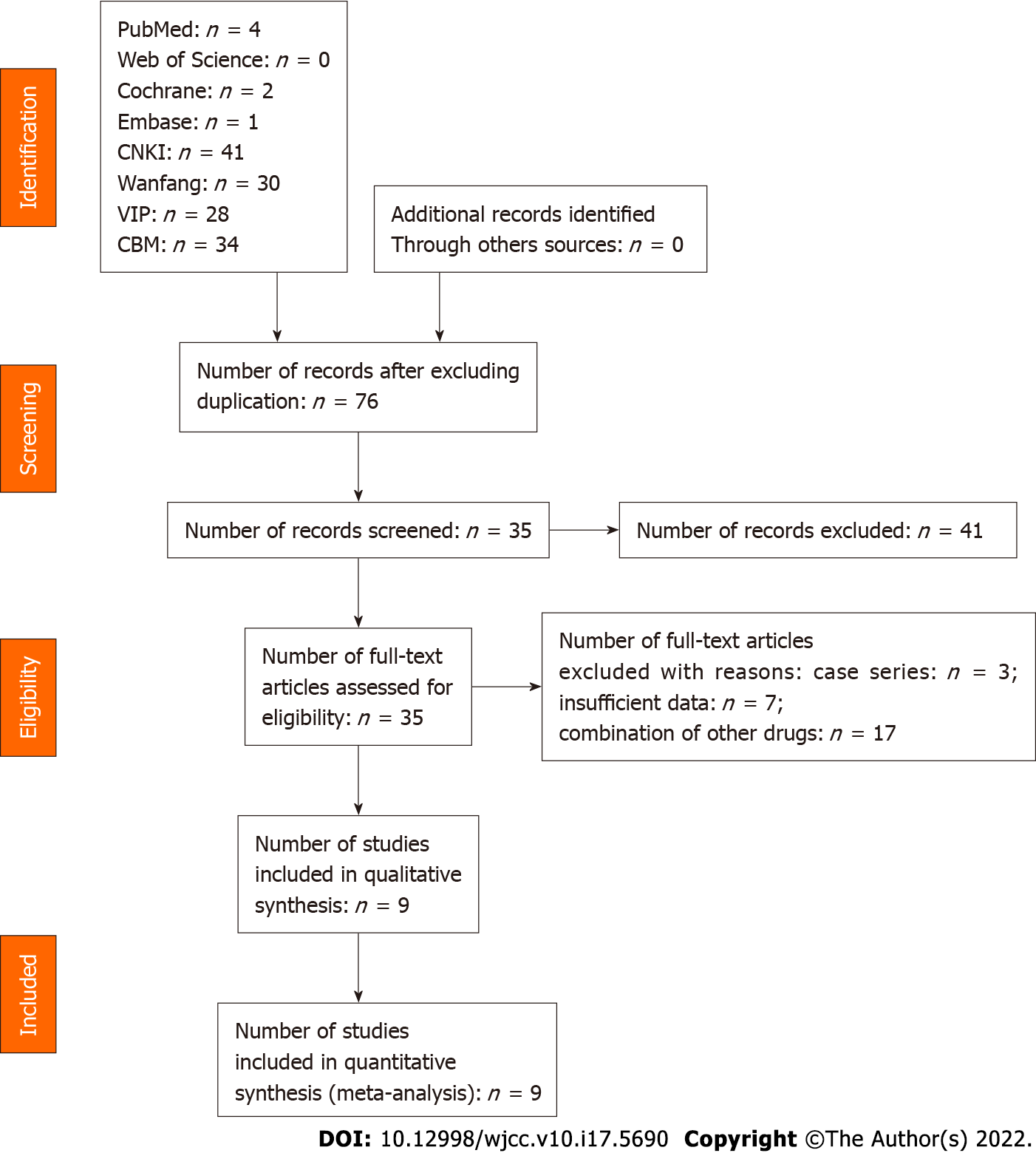
A total of 140 pieces of related literature were initially screened, and 9 randomized controlled studies (RCTs)[15-23] including a total of 936 patients were eventually included for meta-analysis through gradual repeated selection. The literature screening flowchart is shown in Figure 1.
The included studies were single-center RCTs in China, published from 2008 to May 2021. Those articles with incomplete data or that could not be included in statistical analysis, such as duplicates, reviews, conference abstracts, animal experiments and studies involving people with hypothyroidism and other diseases were all excluded, as well as those studies in which the experimental group used Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium and also other drugs or therapies. Finally, 9 RCTs were included[15-23], and the detailed data of the included studies are shown in Table 2.
| Ref. | Intervention measure | Control measure | Average age (yr) | Duration of treatment/ | |
| Experimental group | Control group | ||||
| Zhang et al[15], 2008 | Yougui pills + levothyroxine sodium | Levothyroxine sodium | 53 | 55 | 8 |
| Li et al[16], 2012 | Yougui pills + levothyroxine sodium | Levothyroxine sodium | 68.1 ± 5.3 | 66.7 ± 5.1 | 12 |
| Zhang et al[17], 2015 | Yougui pills + levothyroxine sodium | Levothyroxine sodium | 42.7 ± 3.6 | 42.7 ± 3.6 | |
| Li et al[18], 2016 | Yougui pills + levothyroxine sodium | Levothyroxine sodium | 40.2 ± 9.4 | 40.2 ± 9.4 | |
| Wang et al[19], 2016 | Yougui pills + levothyroxine sodium | Levothyroxine sodium | 40.12 ± 9.50 | 40.57 ± 9.53 | 12 |
| Jiang et al[20], 2017 | Yougui pills + levothyroxine sodium | Levothyroxine sodium | 40.9 ± 5.6 | 40.8 ± 5.8 | 12 |
| Liu et al[21], 2017 | Yougui pills + levothyroxine sodium | Levothyroxine sodium | 37.98 ± 13.83 | 38.88 ± 12.10 | 8 |
| Chen et al[22], 2018 | Yougui pills + levothyroxine sodium | Levothyroxine sodium | 40.88 ± 5.12 | 40.95 ± 5.62 | 12 |
| Shi et al[23], 2018 | Yougui pills + levothyroxine sodium | Levothyroxine sodium | 44.6 ± 12.4 | 45.1 ± 11.9 | 12 |
Revman 5.3 was employed to assess the risk of bias in the included studies as shown in Figure 2A. All 24 studies in Figure 2B are RCTs. The judgment basis for quality evaluation of the 9 articles[15-23] is shown in Table 3.
| Ref. | Randomization method | Blind method | Concealment | Integrity of result data | Selective reporting of results | Other bias |
| Zhang et al[15], 2008 | Just mentioned random | Not mentioned | Unclear | Complete data | Low risk | Unclear |
| Li et al[16], 2012 | Random number table | Not mentioned | Unclear | Complete data | Low risk | Unclear |
| Zhang et al[17], 2015 | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Unclear | Complete data | Low risk | Unclear |
| Li et al[18], 2016 | Just mentioned random | Not mentioned | Unclear | Complete data | Low risk | Unclear |
| Wang et al[19], 2016 | Just mentioned random | Not mentioned | Unclear | Complete data | Low risk | Unclear |
| Jiang et al[20], 2017 | Random number table | Double blind | Unclear | Complete data | Low risk | Unclear |
| Liu et al[21], 2017 | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Unclear | Complete data | Low risk | Unclear |
| Chen et al[22], 2018 | Not mentioned | Double blind | Unclear | Complete data | Unclear | Unclear |
| Shi et al[23], 2018 | Random number table | Not mentioned | Unclear | Complete data | Unclear | Unclear |
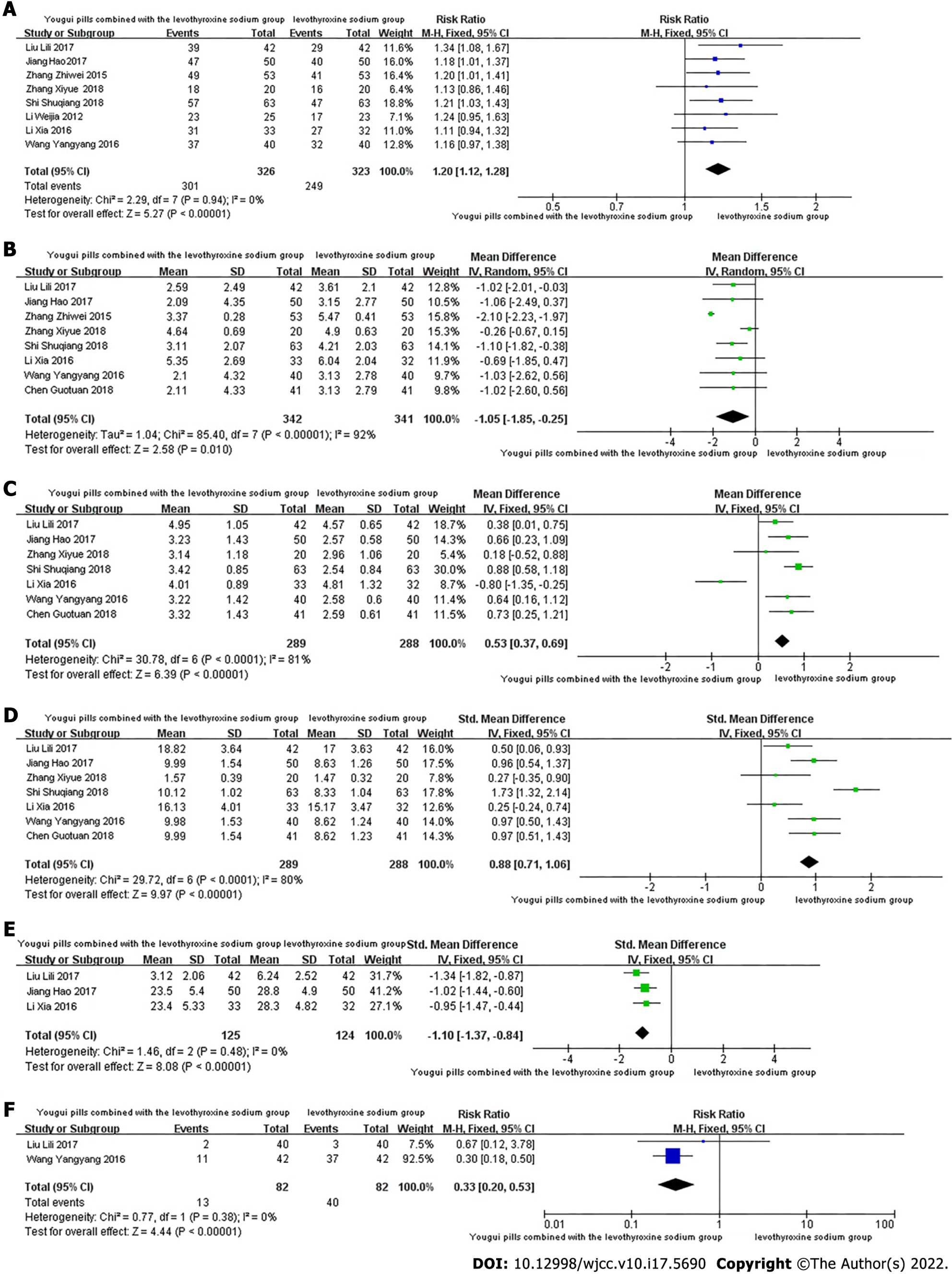
Overall response rate: A total of 8 articles[15-21,23] reported the overall response rate, and the combined effect size was (RR = 1.20, 95%CI: 1.12, 1.28, P < 0.00001. The overall response rate of the Yougui pills combined with the levothyroxine sodium group was significantly higher than that of the levothyroxine sodium group, without significant heterogeneity (I2 = 0%) (Figure 3A).
TSH: TSH levels were concerned in 8 articles[15,17-23], and the effect sizes were combined using the random-effect model. The results showed that in the treatment of hypothyroidism, the level of TSH in the group of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium was significantly lower than in the control group of levothyroxine sodium (MD = -1.05, 95%CI: -1.85, -0.25, P = 0.010), and the combined result was highly heterogeneous (I2 = 92%) (Figure 3B). The sensitivity analysis was performed by excluding each study one by one, and it was found that a study by Zhang[17] was the main source of heterogeneity. After removing this study (MD = -0.62, 95%CI: -0.94, -0.31, P = 0.0001), the heterogeneity of the combined results was acceptable (I2 = 3%), suggesting that this study had no effect on the original conclusions and that the combined results were stable.
FT3: Seven articles[15,17,19-23] reported FT3, thereby combining the effect sizes through the random-effect model. The results showed that when compared with the levothyroxine sodium group Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium in the treatment of hypothyroidism could increase the FT3 levels (MD = 0.53, 95%CI: 0.37, 0.69, P < 0.00001), with high heterogeneity (I2 = 81%) (Figure 3C). By removing each study one at a time for the sensitivity analysis, it was found that the study by Li et al[18] was the main source of heterogeneity. When this study was excluded (MD = 0.65, 95%CI: 0.48, 0.82, P < 0.00001), the heterogeneity of the combined results was acceptable (I2 = 19%), and the original conclusion was not changed, suggesting that the results were robust.
FT4: FT4 was reported in 7 articles[15,17,19-23]. By adopting the random-effect model to combine the effect sizes, the results demonstrated that, when compared with the levothyroxine sodium group, the Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium could significantly increase the FT4 levels in the treatment of hypothyroidism (SMD = 0.83, 95%CI: 0.44,1.22, P < 0.0001], and the combined results were highly heterogeneous (I2 = 80%) (Figure 3D). The sensitivity analysis was carried out by removing each study one at a time, and two studies by Li et al[18] and Shi et al[23]were discovered to be the main sources of heterogeneity. After removing these two studies (SMD = 0.78, 95%CI: 0.57, 0.99, P < 0.0001], the heterogeneity of the combined results was acceptable (I2 = 35%), without changing the original conclusion, suggesting that the results were robust.
TCM symptom scores: Three articles[18,20,21] adopted the TCM symptom scores (unresponsiveness, edema, chills, lethargy, etc) to evaluate the curative effect. Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium were significantly superior to the control group of levothyroxine sodium in reducing syndrome scores, with a combined effect size of (SMD = -1.10, 95%CI: -1.37, -0.84, P < 0.00001], and there was no significant heterogeneity in the combined results (I2 = 0%) (Figure 3E).
Adverse reactions: Two articles[19,21] involved adverse reactions after medication, and the combined effect size was (RR = 0.33, 95%CI: 0.20, -0.53, P < 0.00001. The adverse reactions (dry mouth, hyperhidrosis, insomnia and irritability) were significantly lower in the Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium group than in the levothyroxine sodium group, and there was no significant heterogeneity in the combined results (I2 = 0%) (Figure 3F).
Publication bias: A funnel plot of total efficacy was drawn using Stata 15.0 and further tested by Begg’s and Egger’s tests. The funnel chart appears to be symmetrical, suggesting less possibility of publication bias. The Begg’s and Egger’s tests were adopted to quantitatively analyze the total clinical efficacy of the included studies, and the results showed Begg’s Test P = 0.711 and Egger’s Test P = 0.506, indicating that there was no publication bias (Figures 4 and 5).
Studies have shown that the combination of Yougui pills and Western medicine can produce a synergistic effect, reduce the dosage and duration of hormone usage and reduce or eliminate the adverse reactions caused by hormone usage. However, the value of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium for hypothyroidism is unclear at present. The main findings of this study were as follows: (1) The group of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium had a significantly higher overall response rate than the group of levothyroxine sodium; (2) Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium could significantly improve the adverse symptoms; (3) Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium could significantly increase the levels of FT3 and FT4 and reduce TSH; and (4) When compared to the levothyroxine sodium group, the combination of Yougui pills with levothyroxine sodium could minimize the incidence of adverse reactions significantly. The available evidence shows that Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium are superior to levothyroxine sodium alone in terms of improving the effective rate, reducing adverse reactions and improving clinical symptoms and thyroid function in the treatment of hypothyroidism. It is believed that when Yougui pills are taken with levothyroxine sodium in a treatment plan, Yougui pills can increase the clinical efficacy of levothyroxine sodium and decrease its adverse effects. Therefore, we recommend combining Yougui pills with levothyroxine sodium to treat hypothyroidism.
According to TCM, the mechanism by which Yougui pills taken with levothyroxine sodium can effectively treat hypothyroidism is due to hypothyroidism belonging to the category of consumptive or edema diseases. The medical pathogenesis is the deficiency of kidney yang, the loss of warmth and nourishment of visceral organs, the decline of qi function and even the overflowing of water; kidney yang is the root of yang qi, equivalent to the energy system of the human body, which is just as important to nature as the sun. As a classic TCM prescription for warming and invigorating the kidney and yang, Yougui pills, from the famous physician Zhang Jingyue’s Jingyue Quanshu, are based on warming yang medicines, which are compatible yin-tonifying products in yang-reinforcing medicines and “seeking yang from yin”[24], and its efficacy in the treatment of hypothyroidism has been fully clinically verified.
Modern pharmacological studies of Yougui pills suggest that the mechanism of its curative effect involves the regulation of multiple systems such as nerves, immunity and endocrine. The hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis is an essential branch of the neuroendocrine regulatory circuit that plays a role in thyroid hormone synthesis and release. Studies have verified that deficiency of kidney yang can cause dysfunction of the thalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis[25] and insufficient thyroid hormone secretion[26]. Yougui pills have a dynamic regulatory effect on the function of the pituitary-thyroid axis in rats with kidney-yang deficiency. The blood thyroid hormone level of rats significantly changed following the administration of Yougui pills[27].
Chen et al[28] used thyroid hormone content as an indicator to study the effect of Yougui pills on the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in rats with kidney-yang deficiency, and the experiment showed that the regulating effect of Yougui pills on kidney-yang deficiency syndrome was slow and required a process of dose-effect accumulation. Wu[29] observed that giving Yougui capsules to elderly patients with kidney-yang deficiency significantly increased the level of thyroxine stimulation, which was inversely proportional to the degree of kidney-yang deficiency. The lower the degree of kidney-yang deficiency, the faster the increase in hormone levels.
In the current study, Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium significantly increased FT3 and FT4 while decreasing TSH. Meanwhile, the total treatment efficiency and symptom improvement are better than those of levothyroxine sodium alone. Therefore, we believe that Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium can effectively increase the secretion of hormone secreted in serum, which is conducive to the normal performance of thyroid function as well as significantly improving the metabolic function of tissue cells in the whole body, promoting thyroid microcirculation and restoring the function of the remaining thyroid tissue.
Any medication used to treat disease and restore normal body function carries the risk of causing damage to the body. TCM has typical characteristics of safety and fewer adverse reactions. Two articles in this study reported adverse reactions, and the meta-analysis results showed that the Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium group had significantly fewer adverse reactions (dry mouth, hyperhidrosis, insomnia, irritability) than the levothyroxine sodium group. Considering the limited sample size, Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium may have some rare adverse reactions. Therefore, attention should be paid to adverse drug reactions in clinical application, early detection and treatment to ensure the drug safety of patients.
This study has the following limitations: (1) The quality of the included literature is generally low; (2) There is a certain degree of heterogeneity among different studies; (3) The sample size of the included studies is relatively small, and larger sample studies are needed to provide more precise conclusions; (4) Grey literature was not retrieved; and (5) All included RCTs were open-label, with no treatment control, in which patients were treated with levothyroxine + T preparation alone. Therefore, all patients and investigators are aware of the prescribed treatment, and knowledge of the treatment also affects thyroid hormone and TSH levels. Effect estimates in such “no treatment controlled” trials are usually much larger than in double-blind (placebo-controlled) trials. The aforementioned factors may have a certain influence on the research results. To further validate the results of this study, further multicenter and large-sample studies should be conducted in accordance with RCT research guidelines.
Yougui pills in combination with levothyroxine sodium may be more effective than levothyroxine sodium alone in the treatment of hypothyroidism. The combined treatment can effectively reduce or eliminate the adverse reactions caused by the use of hormones, increase the secretion of hormones in serum and thus significantly improve the clinical symptoms of hypothyroidism. In conclusion, we recommend using levothyroxine sodium in combination with Yougui pills. Although due to the low quality and heterogeneity of the included literature, the findings of this study need to be confirmed by high-quality RCT studies.
Yougui pills are a classic ancient prescription of Ming Dynasty in China, which has been widely used in combination with levothyroxine sodium in the treatment of hypothyroidism. However, the level of evidence in clinical reports is inconsistent, and the credibility is poor. Thus, we conducted this meta-analysis to further confirm the efficacy and safety of Yougui pills and provide higher level evidence.
By strict study selection and quality evaluation, a total of 9 studies were included for further analysis to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety. The results of this meta-analysis could help in rational drug use, the scientific research work and the government’s health care decisions.
We aimed to find the latest and most reasonable treatment plan for the specific clinical problems of hypothyroidism patients. Further, we collected and summarized the homogenous data of the original study of Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium in the treatment of hypothyroidism.
We conducted this meta-analysis to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Yougui pill combined with levothyroxine sodium in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Meta-analysis could combine clinical trial data of multiple small samples to improve the statistical efficiency of the original results and solve the inconsistency of research results. The results from strict meta-analysis have advantage in sample size, coverage, reliability and representativeness.
Compared with pure levothyroxine sodium, Yougui pills combined with levothyroxine sodium could effectively reduce or eliminate the adverse reactions caused by taking hormone, improve serum hormone secretion and significantly improve the clinical symptoms of hypothyroidism. However, this meta-analysis is still limited by relatively low quality and relatively high heterogeneity. Thus, this conclusion needs to be further verified by randomized controlled trial studies.
With the aid of modern scientific research means and systematic evaluation meta-analysis in evidence-based medicine, the rationality and scientific nature of the combined use of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) Yougui pill and Western medicine levothyroxine sodium was studied.
Improving the quality of the original literature is necessary to strengthen the standardization of TCM syndrome diagnosis methods, and high-quality randomized controlled trials of TCM are necessary to evaluate TCM syndromes. The Endocrine Society should develop uniform testing methods to ensure consistency among units and references in China, which would help in enhancing academic exchange among different regions. Although Chinese herbal medicines are generally safe and have relatively few adverse reactions and the mechanisms of adverse effects caused by Chinese medicine are still unclear, we should still pay attention to adverse events in clinical practice and investigate the mechanisms in scientific studies.
We would like to thank all authors of the included primary studies.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Integrative and complementary medicine
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Ciccone MM, Italy; Hegazy AA, Egypt; Trkulja V, Croatia S-Editor: Zhang H L-Editor: Filipodia CL P-Editor: Zhang H
| 1. | Chen J. Clinical Endocrinology. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2011. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 2. | Wang Q, Wang Y. Analysis of the effect of levothyroxine sodium in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Xiandai Yiyao Weisheng. 2017;33:1358-1360. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 3. | Hak AE, Pols HA, Visser TJ, Drexhage HA, Hofman A, Witteman JC. Subclinical hypothyroidism is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction in elderly women: the Rotterdam Study. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132:270-278. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 728] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 684] [Article Influence: 28.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Zeng P, Cao J, Liao M. Intervention study on elderly patients with subclinical hypothyroidism and mild cognitive impairment in Ganzhou City. Qiqihar Yixue Yuan Xuebao. 2020;41:2556-2557. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 5. | Lu Z, Zhong N. Internal Medicine. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2008. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 6. | Pucci E, Chiovato L, Pinchera A. Thyroid and lipid metabolism. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000;24 Suppl 2:S109-S112. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 157] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 160] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Glueck CJ, Streicher P. Cardiovascular and medical ramifications of treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2003;5:73-77. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 3] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Wu P, Zhou X. Research on alternative treatment of hypothyroidism after thyroidectomy. Shiyong Yaowu Yu Linchuang. 2015;18:1329-1331. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 9. | Wu Z, Bian H, Guo Y, Jiang Y, Xie Z, Yang G. Analysis of related causes of hypothyroidism after partial thyroidectomy. Zhongguo Putong Waike Zazhi. 2003;12:366-368. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 10. | Zhang M, Ni Q. Progress in the treatment of hypothyroidism with traditional Chinese medicine. Beijing Zhongyi Yao. 2018;37:851-854. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 11. | Liu Y. The effect of combined Chinese and Western medicine treatment on hypothyroidism. Zhongwai Yixue Yanjiu. 2018;16:135-136. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 12. | Medicine SAoTC. Standards for the diagnosis and efficacy of diseases and syndromes in traditional Chinese medicine. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 1994. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 13. | Shan Z. Guide to "Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Thyroid Diseases in China". Zhognguo Shiyong Neike Zazhi. 2008;28:260. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 14. | Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA; Cochrane Bias Methods Group; Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 18487] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 21395] [Article Influence: 1645.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 15. | Zhang X, Zuo X. Clinical observation of Yougui pill combined with low-dose Youjiale in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Hubei Zhongyi Yao Zazhi. 2008;23-24. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 16. | Li W, Wang Y. Yougui pill combined with low-dose thyroxine in the treatment of 25 cases of senile hypothyroidism. Zhongyi Zazhi. 2012;53:1055-1056. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 17. | Zhang Z. Observation on the effect of combined treatment of 53 cases of hypothyroidism with Youlejia and Yougui Pills. Medical Aesthetics and Cosmetology. 2015;3:614-615. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 18. | Li X, Lou J, Chen Y, Wu C, Jiang M. Clinical Observation on the Treatment of Primary Hypothyroidism (Kidney Yin and Yang Deficiency Syndrome) with Yougui Pills. Yatai Chuantong Yiyao. 2016;12:118-119. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 19. | Wang Y, Zhu W. Clinical observation of Yougui pill combined with levothyroxine sodium tablets in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Xin Zhongyi. 2016;48:90-92. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 20. | Jiang M, Wang R, Wang F, Li S. The clinical effects of Yougui Pills combined with levothyroxine sodium tablets in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Zhongguo Yiyao Daobao. 2017;14:165-168. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 21. | Liu L. Observation on the clinical efficacy of the method of warming the kidney and yang in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Thesis, Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2017. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 22. | Chen G. Clinical effects of Yougui Pills combined with levothyroxine sodium tablets in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Linchuang Yiyao Wenxian Dianzi Zazhi. 2018;5:55. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 23. | Shi S, Du Z. Study on the clinical effect of Yougui Pill plus or minus combined with levothyroxine sodium in the treatment of hypothyroidism. Zhongguo Heli Yongyao Tansuo. 2018;15:23-26. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 24. | Xie M, Zhou R. Prescriptions. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2014. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 25. | Zhou X, Jia X, Li M. Clinical effect of Yougui pill in the treatment of TPOAb-positive subclinical hypothyroidism. Zhongguo Jihua Shengyu Xue Zazhi. 2019;27:457-460. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 26. | Li F, Zhang Y, Li Y, Chu Y, Wang F, Li H. Modern research progress in pharmacology of Yougui Pills. J Tradit Chin Med. 2017;45:108-112. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 27. | Zhai X, Huang Y, Shi J, Jia T, Lou Y, Dong Q. Regulation of Morinda officinalis on hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in rats with kidney-yang deficiency. Zhong Cheng Yao. 2017;39:233-237. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 28. | Chen L, Wang X, Ma N, Liao C, Liu J, Lai B, Huang M, Chen S. Dynamic effects of Yougui Pill on hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in rats with kidney-yang deficiency. Guangdong Yixue Yuan Xuebao. 2016;32:771-774. [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 29. | Wu T. Effect of Yougui Capsule on Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis Function in Elderly Men with Kidney Yang Deficiency. Thesis, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2015. [Cited in This Article: ] |